Gram Negative Bacilli Treatment Uti
Gram negative bacilli treatment uti. Gram negative bacillus 100000 CFUml Lactose fermenting gram negative rod. One area where the approach to antibiotic use needs to be readdressed is the use of combination antibiotic therapy which generally consists of a β-lactam and an aminoglycoside or fluoroquinolone for the treatment of infections with Gram-negative bacteria. See also Introduction to Urinary Tract Infections.
Kidney stones and obstructive uropathy may be contributors. The cut-off for a high bacterial count in most UTIs is 100000 per mL which is the same as 10 million per L. However with only a single gram negative organism even lower numbers usually are significant so this result indicates probable UTI that needs treatment.
Coli cause most uncomplicated cystitis and. Discuss with your doctor. Combination antibiotic therapy for invasive infections with Gram-negative bacteria is employed in many health care facilities especially for certain subgroups of patients including those with neutropenia those with infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa those with.
Linezolid is prescribed sparingly because it has several adverse side-effects such as nausea headaches diarrhea anemia accompanied by severely decreased white blood cell and platelet counts visual impairments and peripheral neuropathy. FYI CFU colony forming units ie. This membrane is what makes it harder to treat infections caused by gram-negative bacteria.
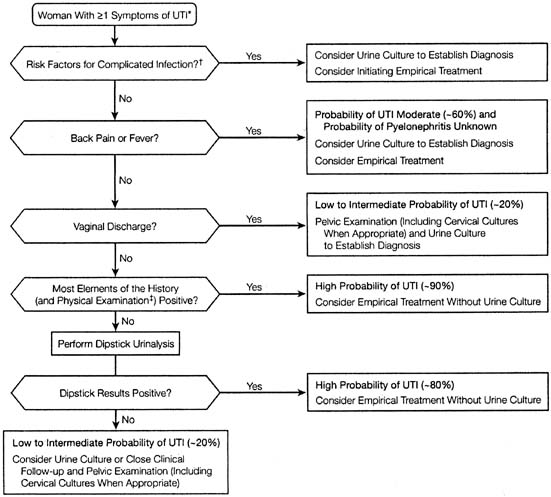
Escherichia coli or E. And Urinary Tract Infection in Children. Antibiotics are begun presumptively in all toxic-appearing children and in nontoxic children with a probable UTI positive leukocyte esterase nitrites or pyuria.
Gram negative bacilli rarely occur by the hematogenous route. It also describes best practice in antimicrobial prescribing. Gram negative rods 1 and 2 equal one organism.
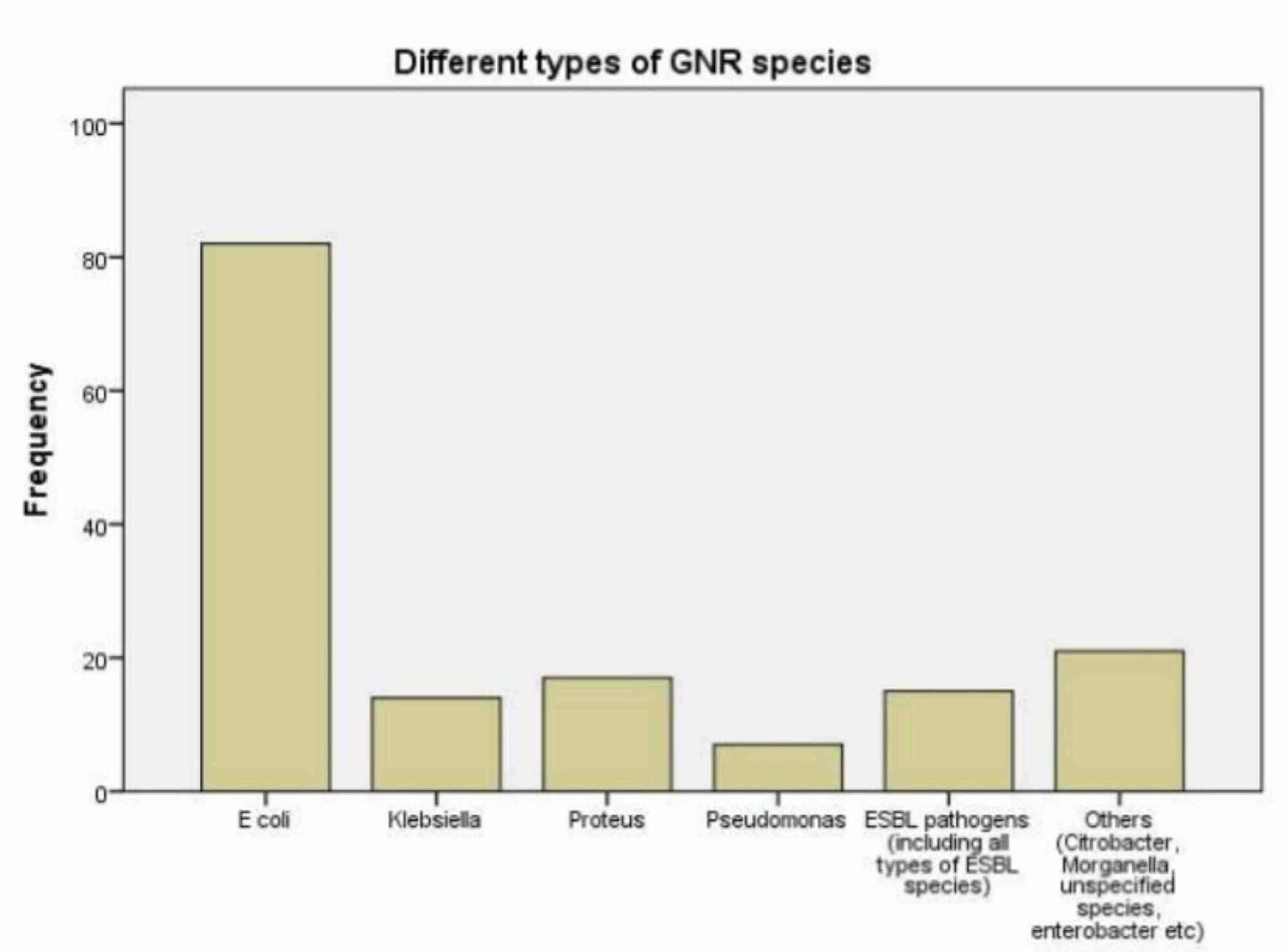
Pathogenic organisms revealed by urine culture include Gram-negative bacilli E coli Proteus Klebsiella others. Numerous white blood cells found on microscopic wet mount examination of vaginal discharge.
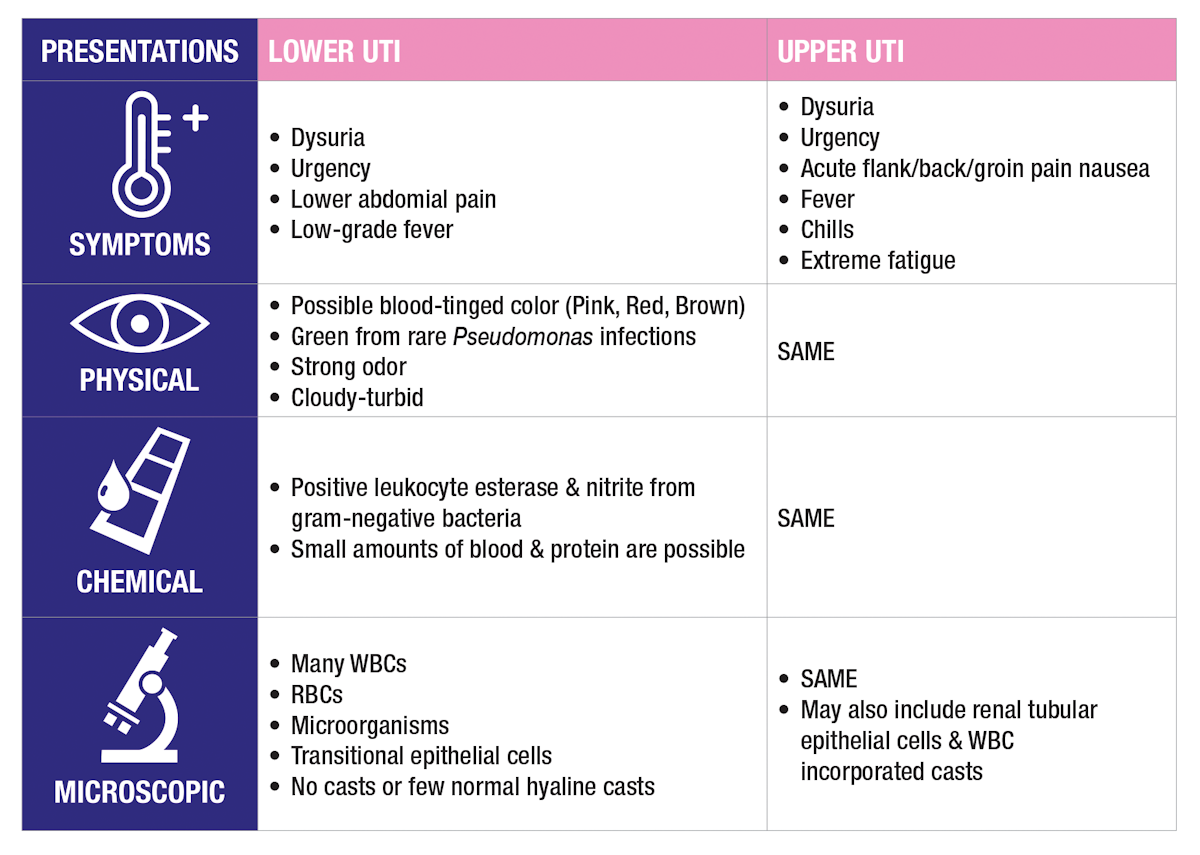
Gram-negative bacilli Pyelonephritis UTI with the presence of upper urinary tract symptoms such as fever CVA tenderness nausea vomiting and signs of sepsis Same pathogens as for complicated UTI Catheter-Associated UTI CA-UTI UTI in patients with indwelling urethral or suprapubic catheters or those who receive intermittent catheterization typically presents without usual lower.
The aim of this review paper was to summarize current developments in the global burden of UTI the diagnostic aspects of these infectious pathologies the possible etiological agents and their virulence determinants with a special focus on the members of the Enterobacterales order current guidelines and quality indicators in the therapy of UTIs and the emergence of multidrug resistance in. The cut-off for a high bacterial count in most UTIs is 100000 per mL which is the same as 10 million per L. Enterococcus species 40000- 50000 CFUml. Antibiotics are begun presumptively in all toxic-appearing children and in nontoxic children with a probable UTI positive leukocyte esterase nitrites or pyuria. Some examples of gram-negative bacteria that cause urinary tract infections include. This membrane is what makes it harder to treat infections caused by gram-negative bacteria. Numerous white blood cells found on microscopic wet mount examination of vaginal discharge. Although carbapenems were not the first line choices for uncomplicated cystitis and pyelonephritis in women according to the IDSA guideline they were good alternatives against multidrug resistant Gram-negative bacilli that caused UTIs. Appropriate antimicrobial treatment for UTIs increases the probability of suppression and cure 23.
Combination antibiotic therapy for invasive infections with Gram-negative bacteria is employed in many health care facilities especially for certain subgroups of patients including those with neutropenia those with infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa those with. One area where the approach to antibiotic use needs to be readdressed is the use of combination antibiotic therapy which generally consists of a β-lactam and an aminoglycoside or fluoroquinolone for the treatment of infections with Gram-negative bacteria. Urinary tract infections in women develop when uropathogens from the fecal flora colonize the vaginal introitus and displace the normal flora diphtheroids lactobacilli coagulase-negative staphylococci and streptococcal species. 36 linhas If gram-negative organism a fluoroquinolone. This is an eligible specimen because there is not greater than 2 organisms of which one is a bacterium of 100000 CFUml. Treatment of urinary tract infection is aimed at eliminating the acute infection preventing urosepsis and preserving renal parenchymal function. Numerous white blood cells found on microscopic wet mount examination of vaginal discharge.

























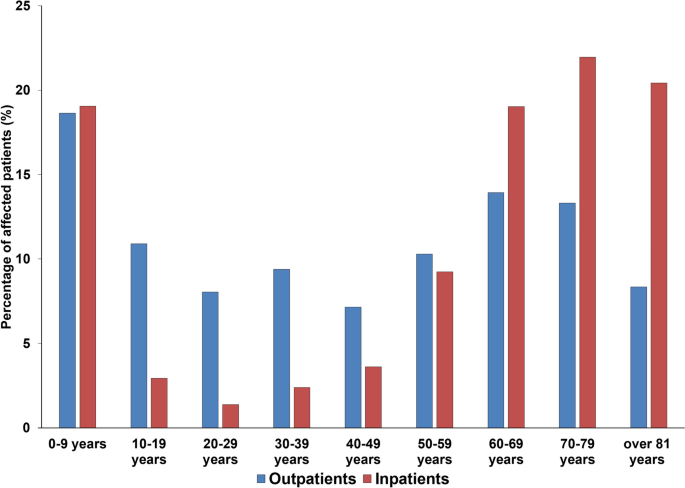


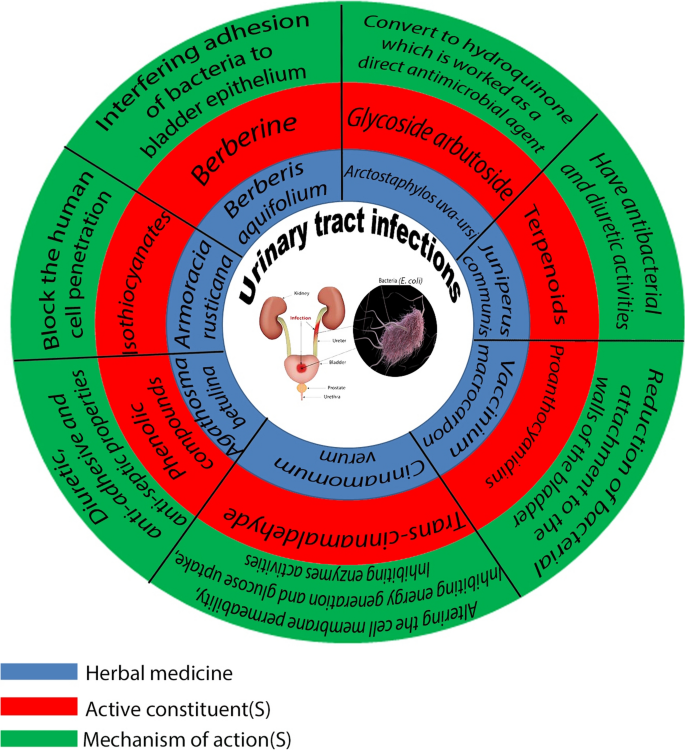

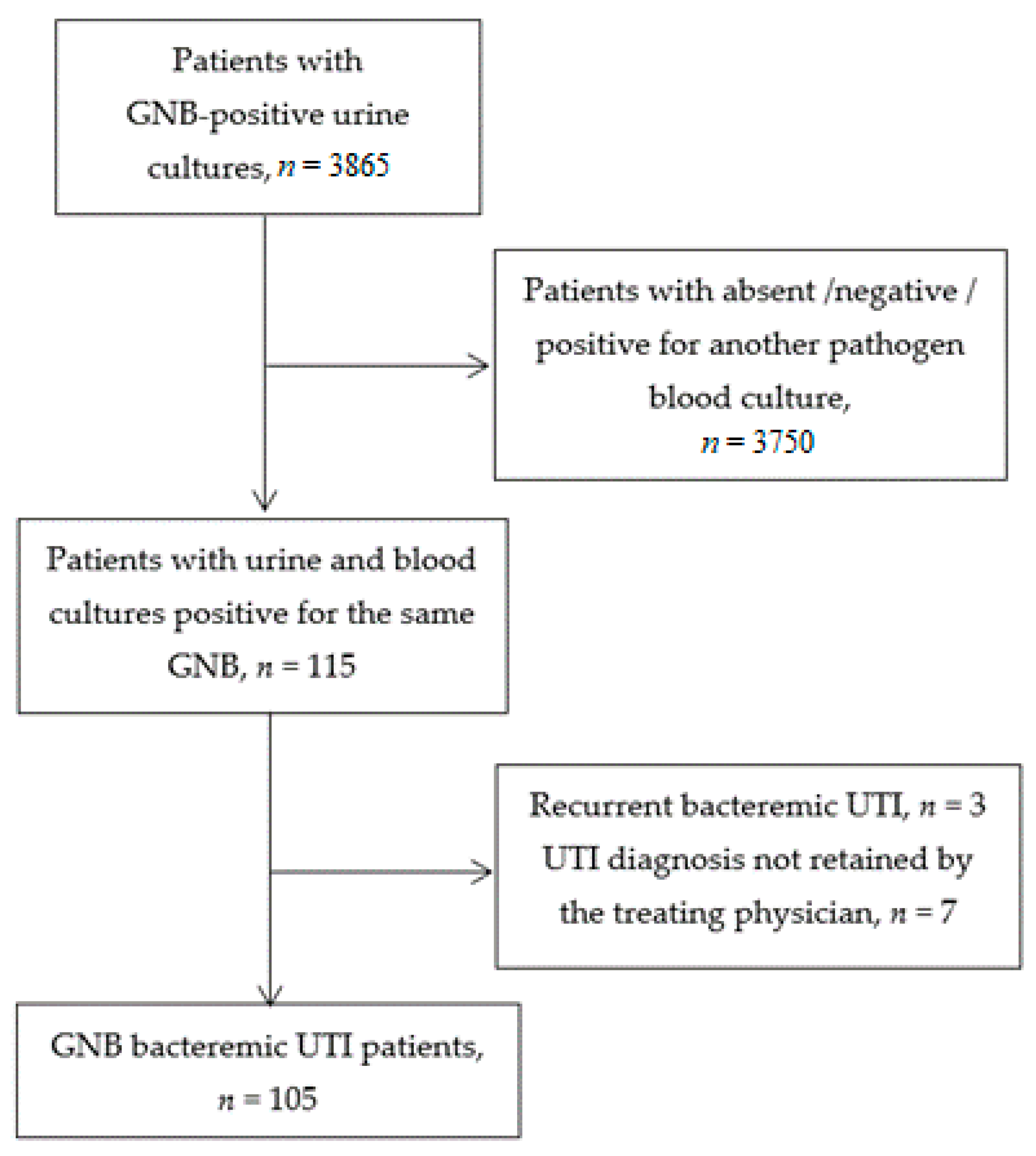
Posting Komentar untuk "Gram Negative Bacilli Treatment Uti"