Autosomal Dominant Tubulointerstitial Kidney Disease
Autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease. Autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease ADTKD is a. In the teenage years patients may develop a. Kidney and Urinary Diseases 281 Digestive Diseases 252.
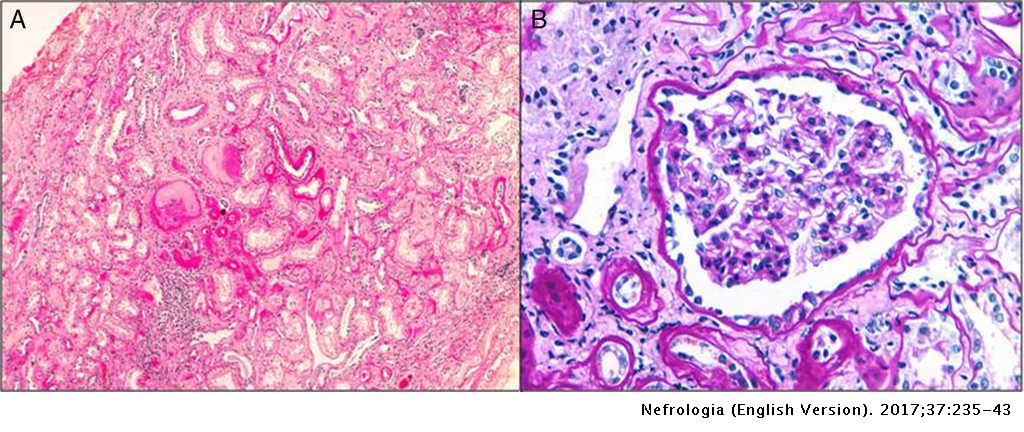
Autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease. Signs and symptoms of all forms of ADTKD include slowly worsening kidney disease often becoming apparent by the teenage years that ultimately results in end-stage kidney disease at some time between. Autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease ADTKD is a group of uncommon genetic disorders characterized by progressive decline in kidney function and autosomal dominant inheritance.
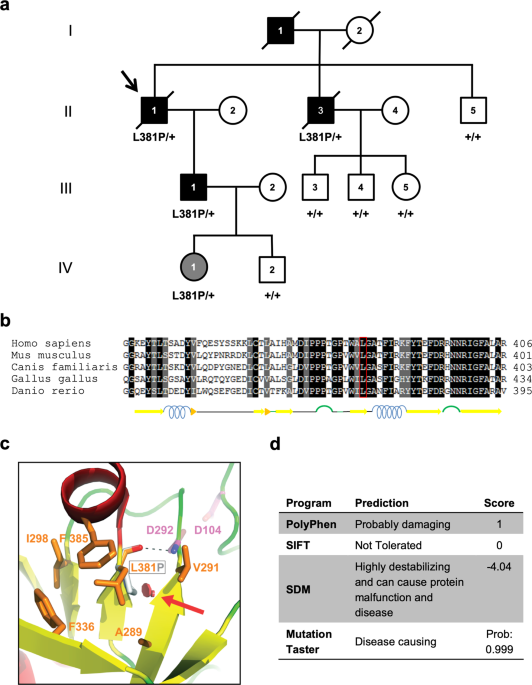
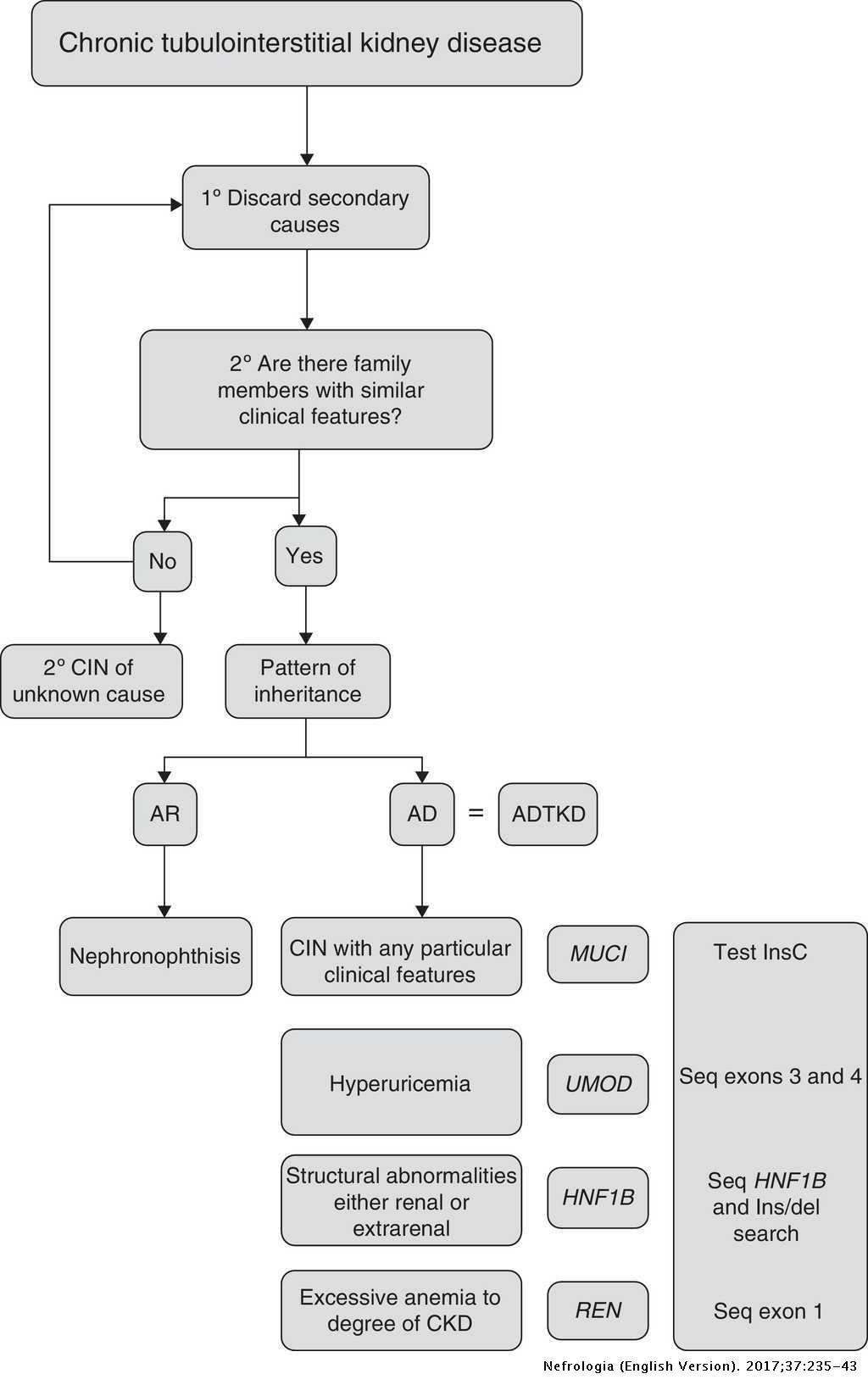
Autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease ADTKD describes a group of diseases that affect the tubules of the kidney. These conditions have the following characteristics. Autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease due to REN mutations ADTKD-REN is an inherited disorder that causes anemia mildly low blood pressure and an increased chance to develop kidney failure in childhood.
Childhoodadolescent onset the more common presentation caused by REN variants encoding the signal peptide or prosegment. It is one of several diseases now termed autosomal dominant tubu-lointerstitial kidney disease as proposed by a KDIGO Kidney Disease. Neither the national or global prevalence of these diseases has been determined.
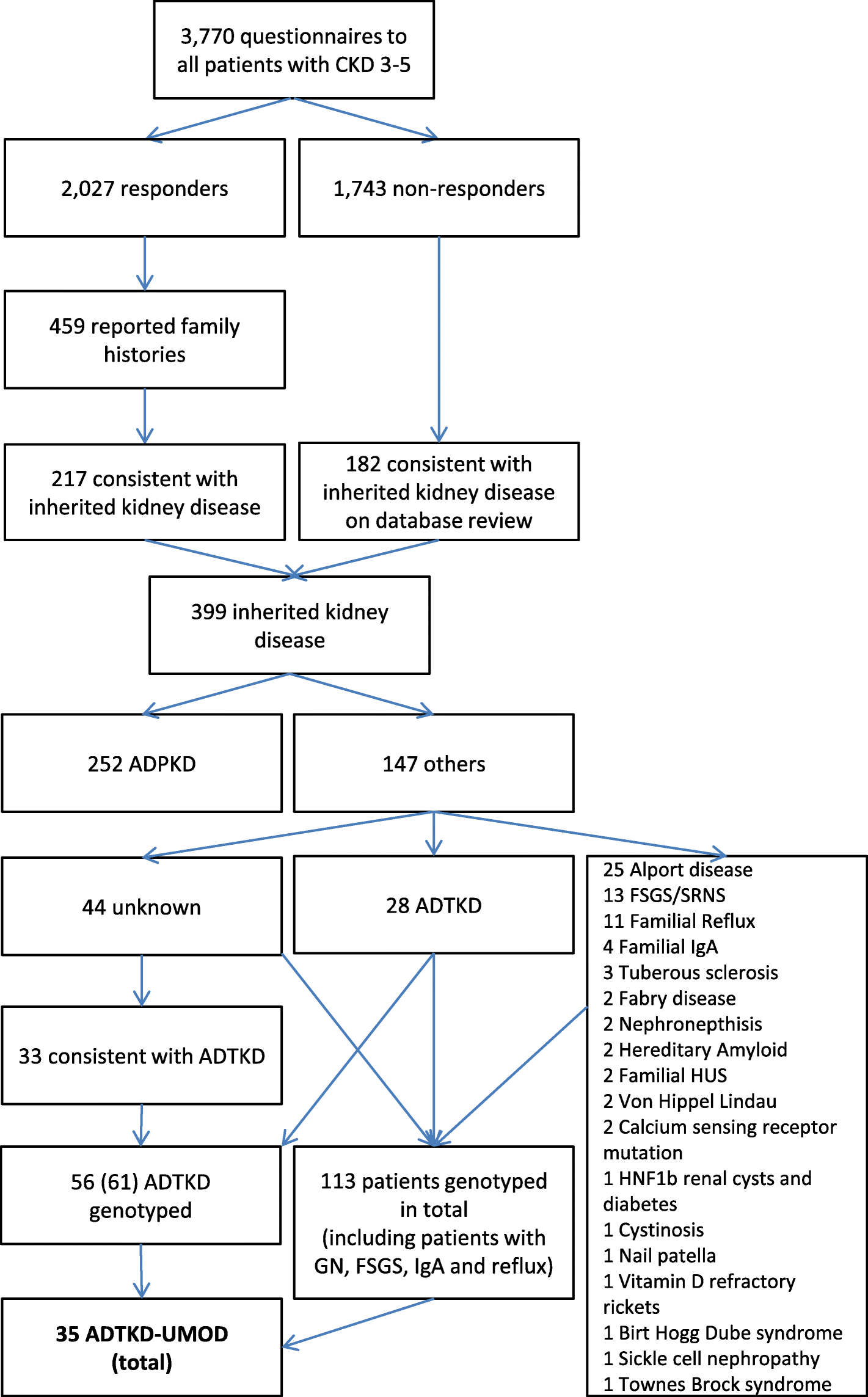
We aimed to establish a database of patients with ADTKD in Ireland and report the clinical and genetic characteristics of. Autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease ADTKD is a group of inherited conditions that affect the tubules of the kidneys causing the kidneys to gradually lose their ability to work. Autosomal Dominant Tubulointerstitial Kidney Disease UMOD-Related - PubMed ADTKD-UMOD is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner.
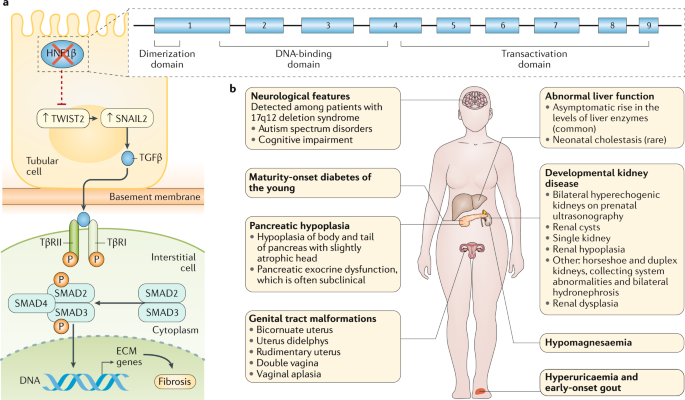
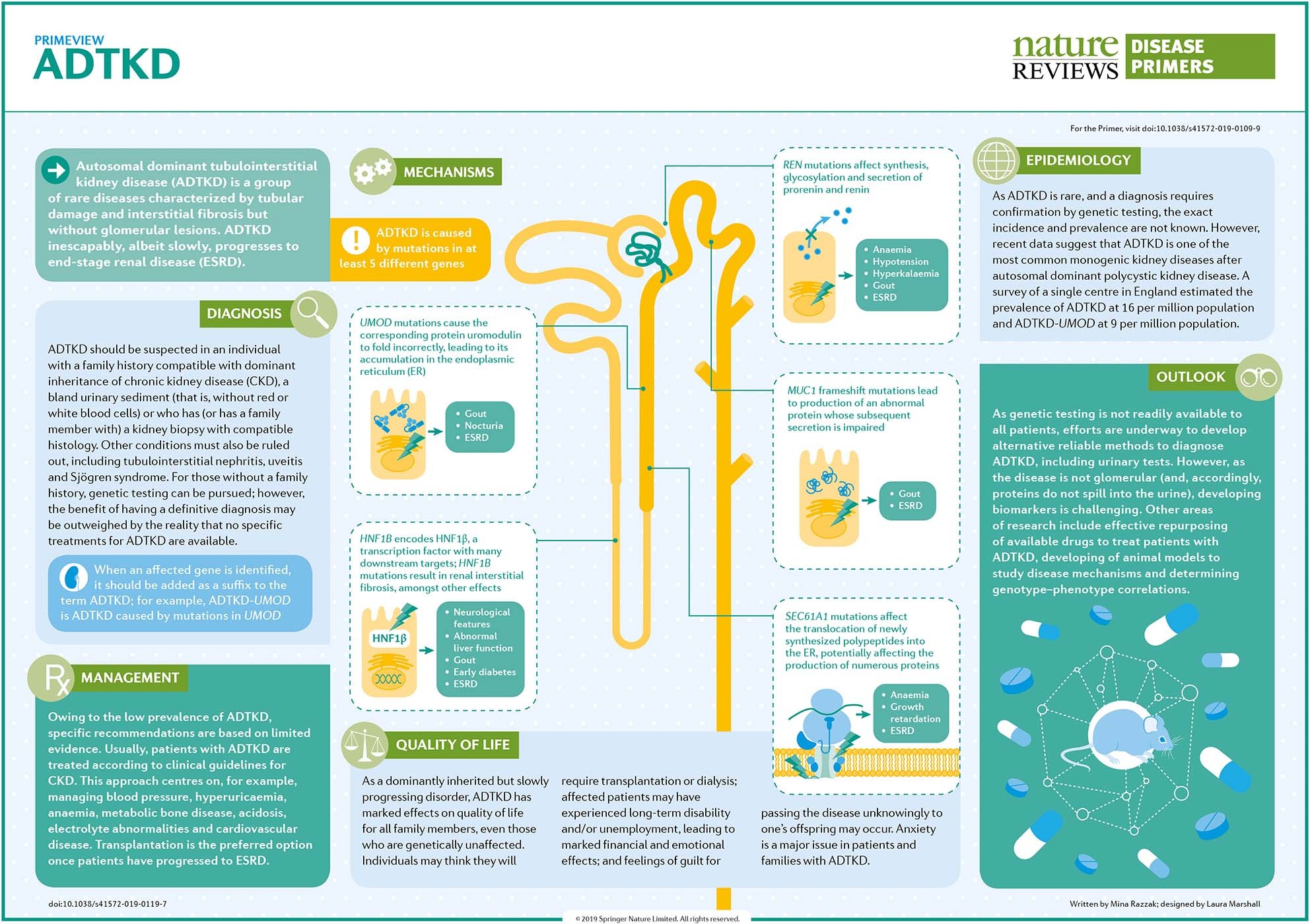
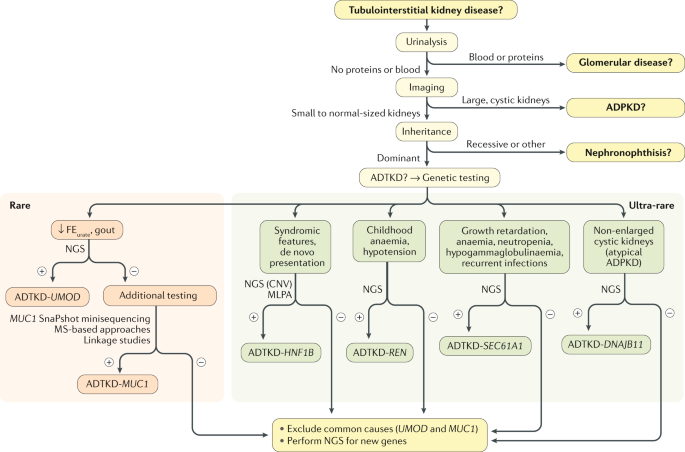
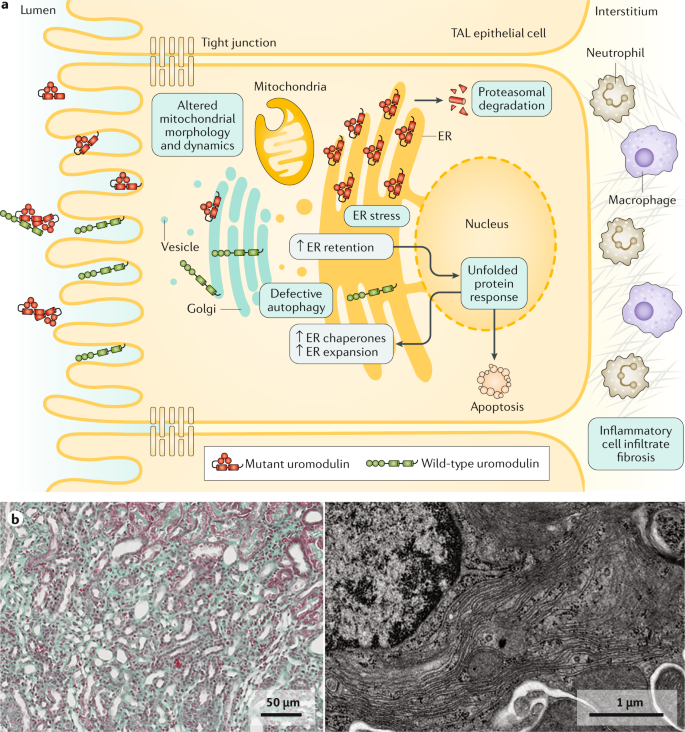
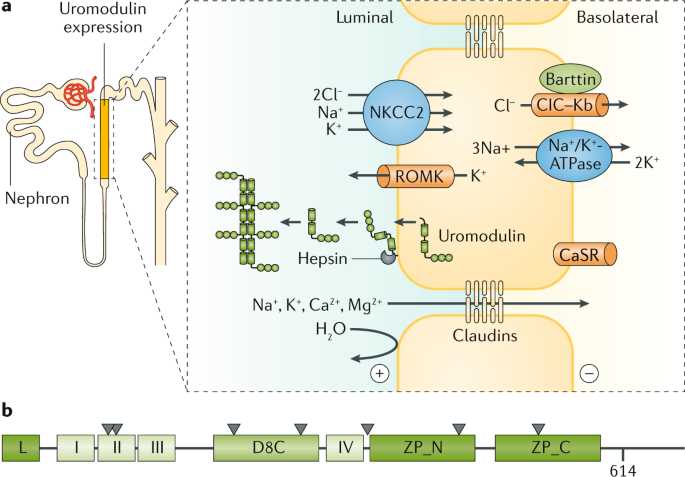
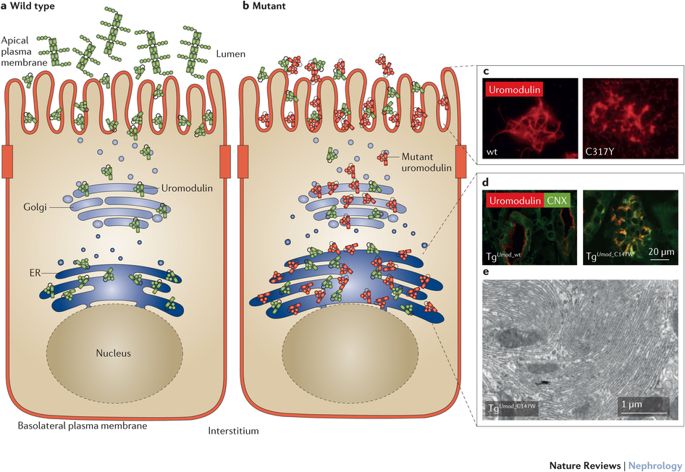
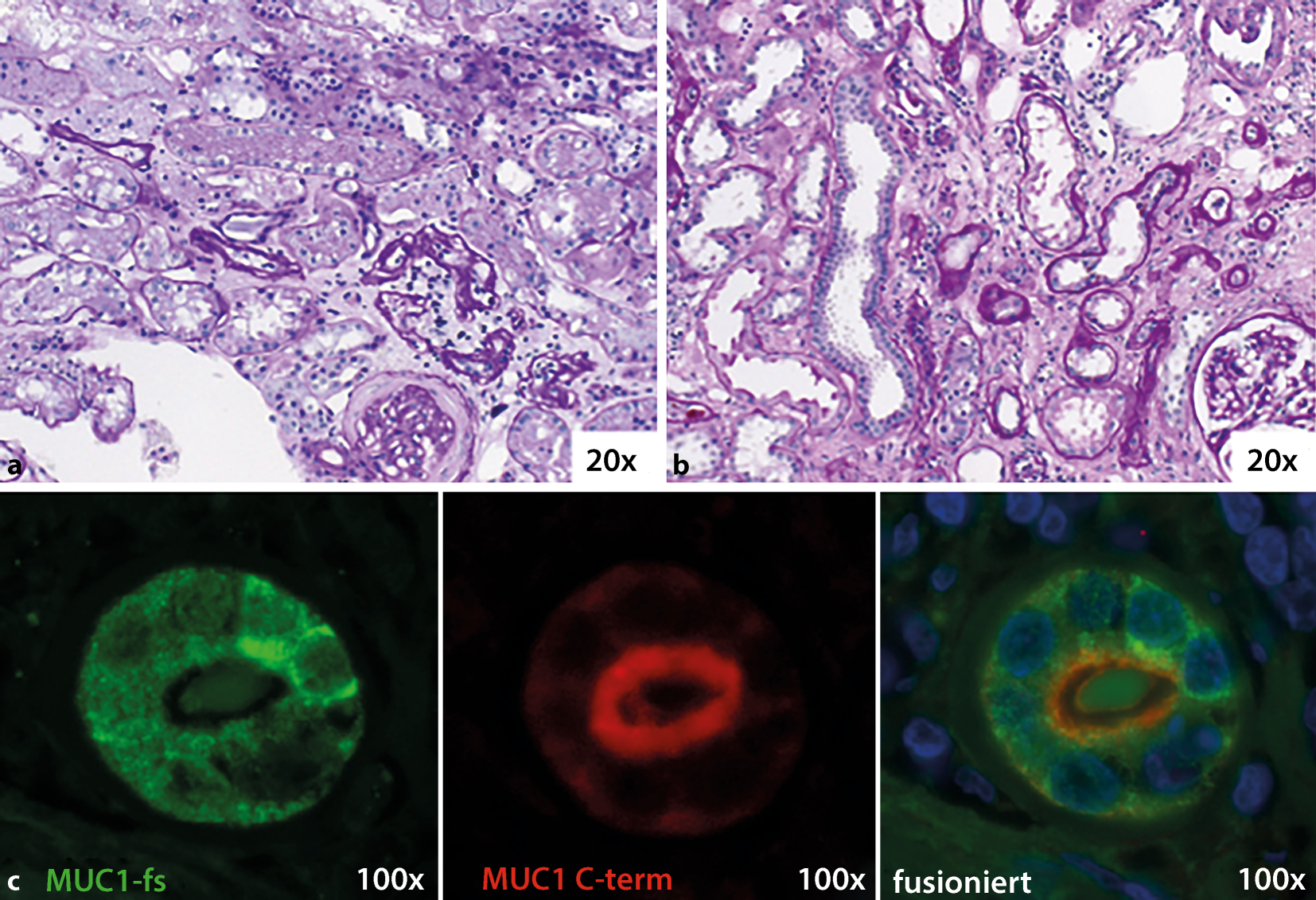
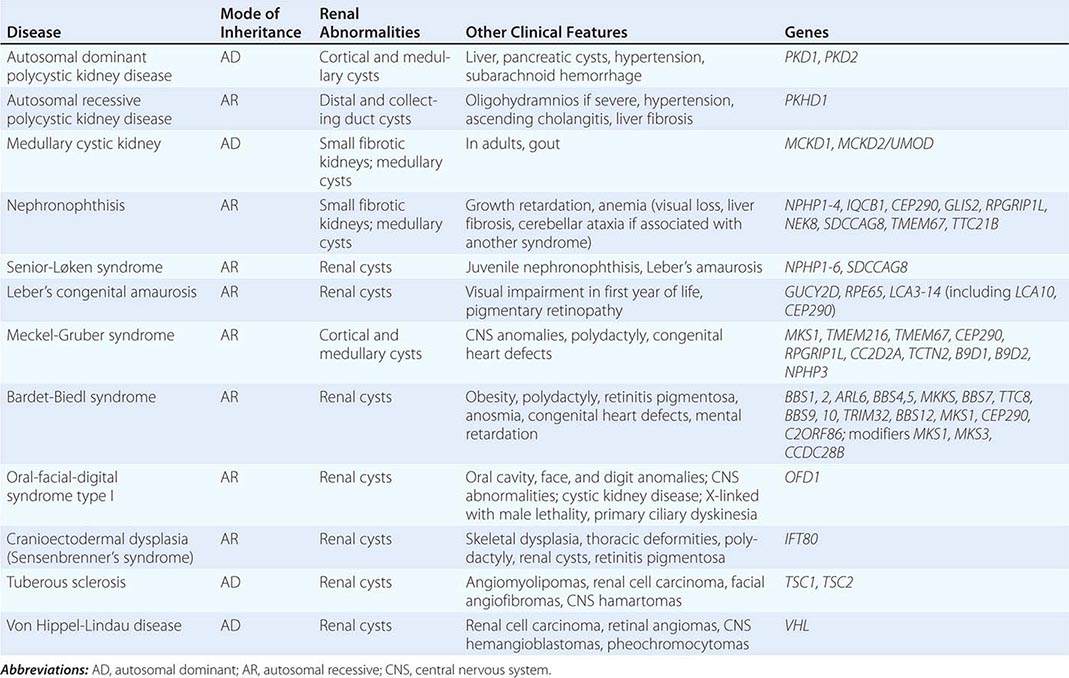
Rare autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease is caused by mutations in the genes encoding uromodulin UMOD hepatocyte nuclear factor-1b HNF1B renin REN and mucin-1 MUC1. Autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease UMOD ADTKD-UMOD is characterized by a normal urinalysis and slowly progressive chronic kidney disease CKD usually first noted in the teen years and progressing to end-stage renal disease ESRD between the third and seventh decades Kidd et. Autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney diseases.
Autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease ADTKD is a group of genetic kidney diseases that cause progressive loss of kidney function. The two clinical presentations observed in autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease REN ADTKD- REN correlate with the renin protein domains affected by the causative REN variants.
In the teenage years patients may develop a.
Autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease ADTKD is a group of genetic kidney diseases that cause progressive loss of kidney function. Neither the national or global prevalence of these diseases has been determined. In the teenage years patients may develop a. Kidney and Urinary Diseases 281 Digestive Diseases 252. Mucin 1 kidney disease previously referred to as medullary cystic kidney disease type 1 is a rare hereditary kidney disease. Autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease Abstract. Autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease ADTKD is a recently defined entity that includes rare. There are approximately 500 families in the United States suffering from this condition and the prevalence in other countries is likely to be similar. Autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease due to REN mutations ADTKD-REN is an inherited disorder that causes anemia mildly low blood pressure and an increased chance to develop kidney failure in childhood.
Diagnosis classification and managementA KDIGO consensus report Rare autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease is caused by mutations in the genes encoding uromodulin UMOD hepatocyte nuclear factor-1β HNF1B renin REN and mucin-1 MUC1. Each child of an affected individual has a 50 chance of inheriting the pathogenic variant. Neither the national or global prevalence of these diseases has been determined. Improving Global Outcomes consensus report in 2014. Autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease Abstract. Autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease UMOD ADTKD-UMOD is characterized by a normal urinalysis and slowly progressive chronic kidney disease CKD usually first noted in the teen years and progressing to end-stage renal disease ESRD between the third and seventh decades Kidd et. They are inherited in an autosomal dominant manner.






























Posting Komentar untuk "Autosomal Dominant Tubulointerstitial Kidney Disease"