Voltage Gated Potassium Channel Antibody Syndrome
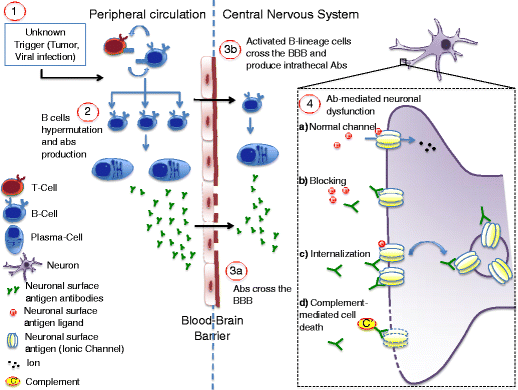
Voltage gated potassium channel antibody syndrome. Recent advances have supported the pathologic mechanism of VGKC in these disorders their response to therapy. Syndromes from antibodies to voltage-gated potassium channels include neuromyotonia NMT limbic encephalitis LE and Morvan syndrome MVS. We aim to present a case of a 53-year-old man with positive antivoltage-gated potassium channel VGKC complex antibodies who initially presented with symptoms of psychotic mania.
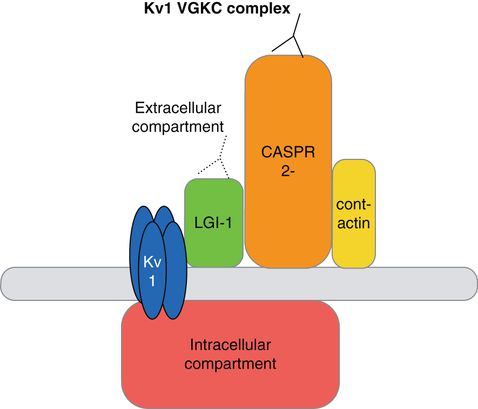
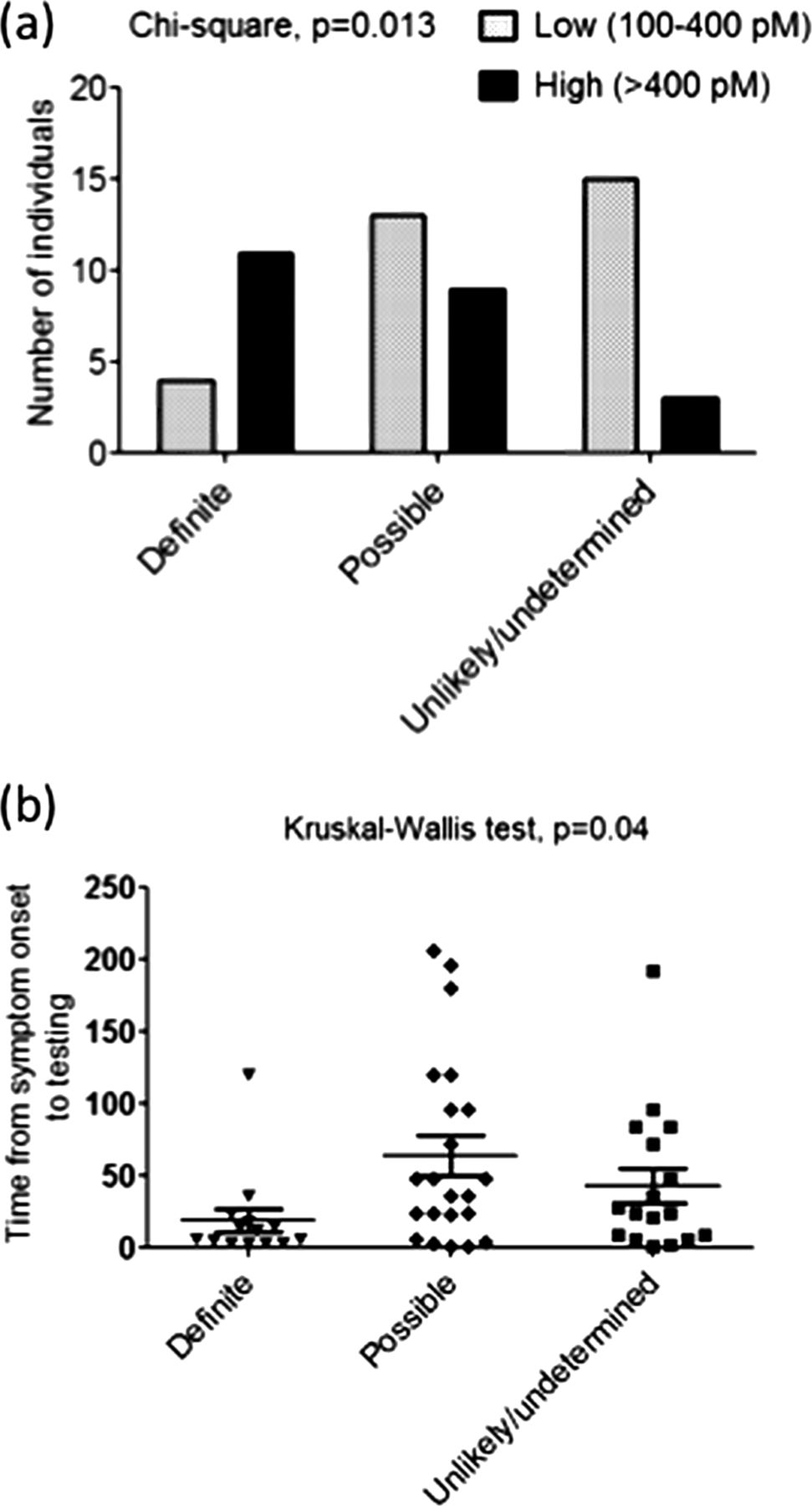
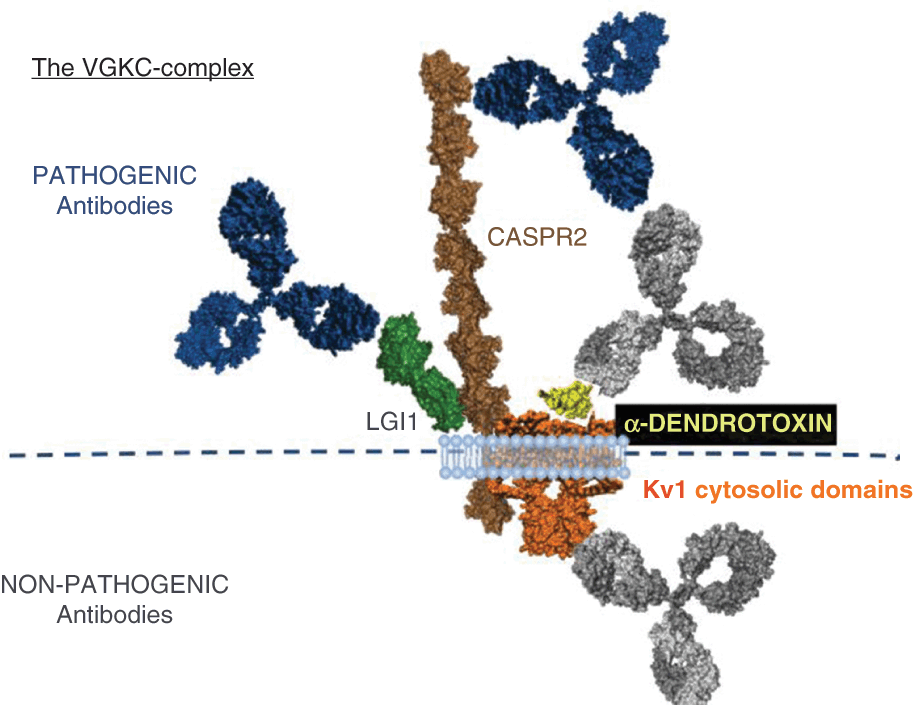
Also known as. Antibodies against contactin-associated protein-like 2 CASPR2 a subtype of voltage-gated potassium channel VGKC complex are found in a significant proportion of patients with Morvans syndrome and are thought to play a key role in peripheral as well as central clinical manifestations. However there are patients with positive levels in whom the significance is uncertain.
Over the past decade antibodies against voltage-gated potassium channels VGKCs have been reported in a number of neurologic syndromes such as neuromy-otonia limbic encephalitis and Morvans syndrome. Diseases Associated with Antibodies to Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels P otassium channelopathies are caused either by autoantibodies directed against the potassium channels or by mutations in their encoding genes. Subsequently they were found in patients with PNH plus psychosis insomnia and dysautonomia collectively termed Morvans.
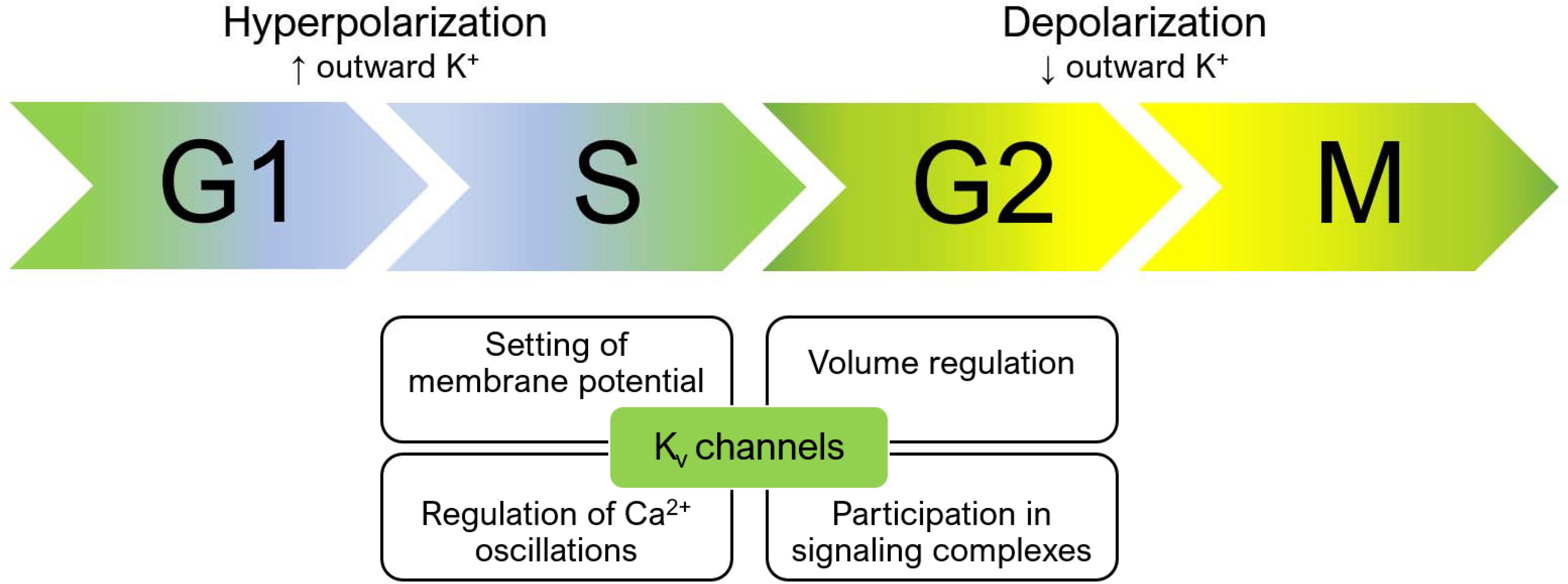
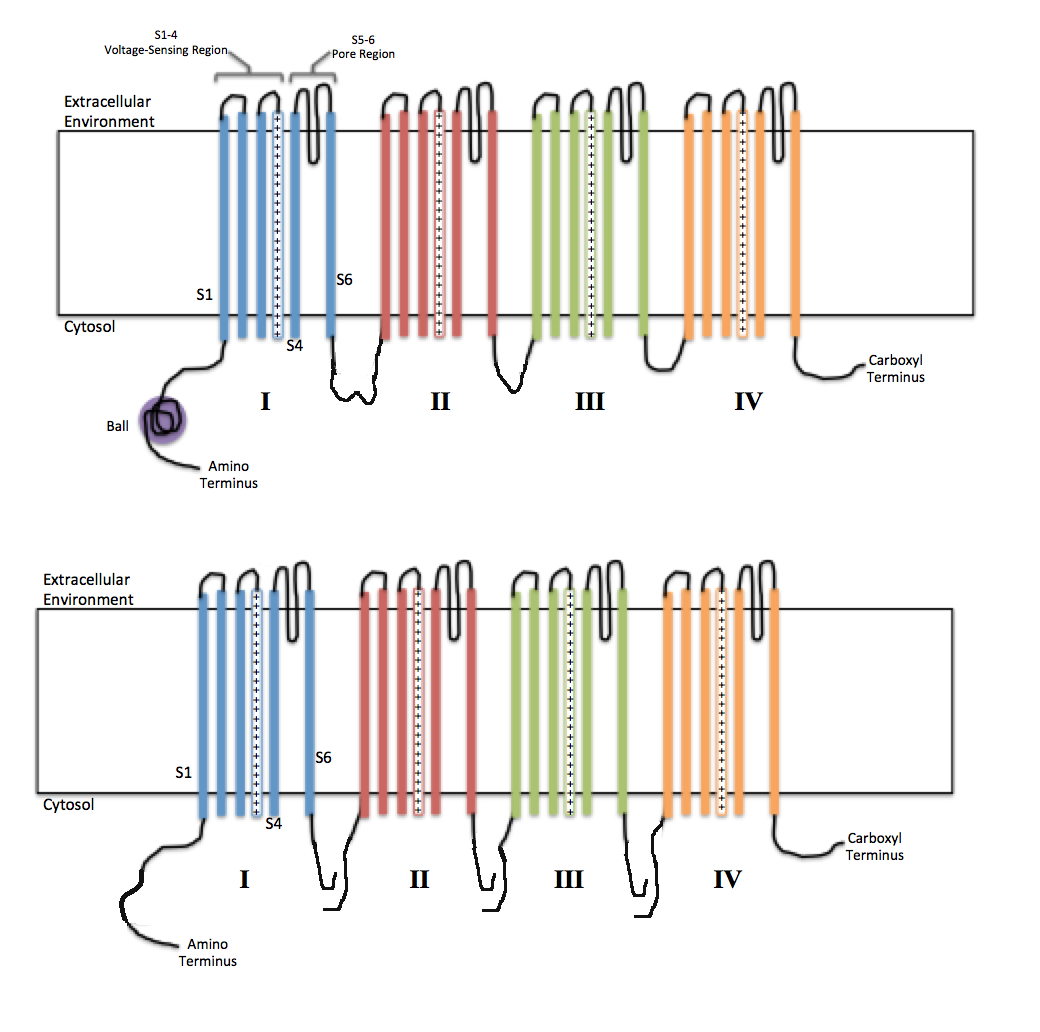
Voltage-gated potassium channels VGKCs are a family of membrane proteins responsible for controlling cell membrane potential. The presence of antibodies Ab against neuronal VGKC complexes aids in the diagnosis of idiopathic and paraneoplastic autoimmune neurologic disorders. We present a case of voltage-gated potassium channel VGKC antibody Ab syndrome which is a form of autoimmune non-paraneoplastic encephalitis that presents with acute or subacute memory loss confusion agitation and psychiatric symptoms.
Antibodies to voltage-gated potassium channels VGKC can cause 3 major syndromes. Cited in 1521 publications. Ad Available as HRP FITC PE Agarose and multiple 6 AlexaFluor conjugates.
Voltage gated K channel complex antibodies Potassium channel complex antbodies are found in patients with acquired neuromyotonia 40-50 percent Morvans syndrome limbic encephalitis paraneoplastic and idiopathic as well as patients with facio-brachial dystonic seizures FBDS. Benign neonatal febrile convulsions1 and hereditary deaf-ness syndromes2 are associated with mutations in the. Voltage-gated potassium channel antibody disorders include limbic encephalitis faciobrachial dystonic seizures and peripheral nerve hyperexcitability disorders that may occur following immunotherapy andor plasmapheresis.
Afterdischarges and continuous motor activity on electromyogram LE encephalopathy with. A radioimmunoassay RIA to detect antibodies against what was initially believed to be voltage-gated potassium channels VGKC in patients with neuromyotonia was established 20 years ago.
Syndromes from antibodies to voltage-gated potassium channels include neuromyotonia NMT limbic encephalitis LE and Morvan syndrome MVS.
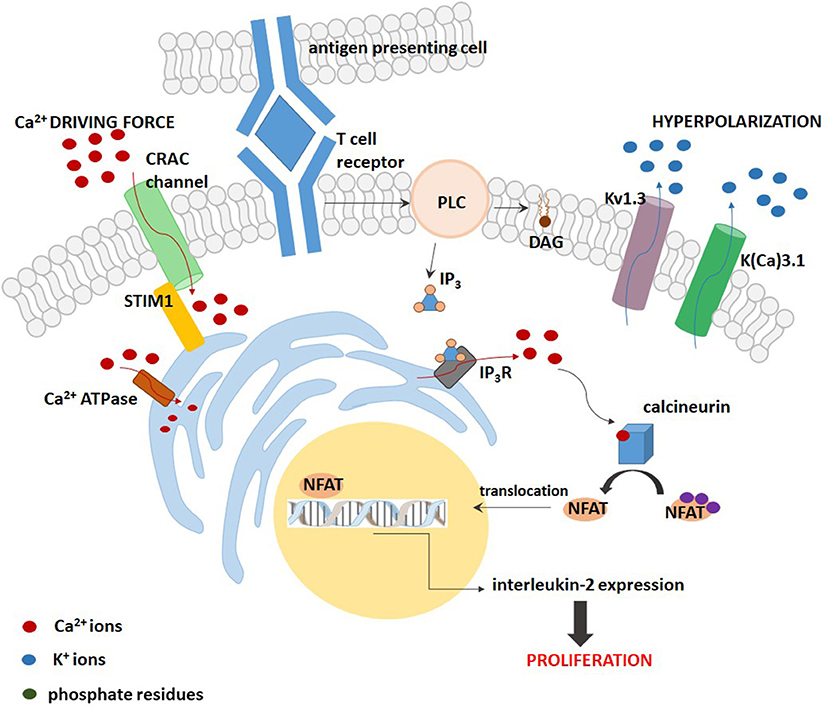
Voltage-Gated Potassium Channel VGKC Antibody - Limbic encephalitis LE is a paraneoplastic neurological syndrome often associated with small cell lung carcinoma and more rarely with testicular breast and other tumors. Voltage-gated potassium channels VGKCs represent a group of tetrameric signaling proteins with several functions including modulation of neuronal excitability and neurotransmitter release. Neuromyotonia NMT limbic encephalitis LE and Morvan syndrome MVS with the latter encompassing elements of the others. Benign neonatal febrile convulsions1 and hereditary deaf-ness syndromes2 are associated with mutations in the. Voltage-gated potassium channels VGKCs are a family of membrane proteins responsible for controlling cell membrane potential. Recent advances have supported the pathologic mechanism of VGKC in these disorders their response to therapy. Subsequently they were found in patients with PNH plus psychosis insomnia and dysautonomia collectively termed Morvans. We aim to present a case of a 53-year-old man with positive antivoltage-gated potassium channel VGKC complex antibodies who initially presented with symptoms of psychotic mania. Voltage-gated potassium channel VGKC-complex antibodies can be associated with a range of immunotherapy-responsive clinical presentations including limbic encephalitis Morvans syndrome and acquired neuromyotonia.
Six weeks post-psychiatric symptomatology he presented with neurological symptoms such as faciobrachial jerking and tonic-clonic seizure. Six weeks post-psychiatric symptomatology he presented with neurological symptoms such as faciobrachial jerking and tonic-clonic seizure. Voltage-Gated Potassium Channel VGKC antibodies are associated with neuromuscular weakness as found in neuromyotonia also known as Issacs syndrome and Morvan syndrome. Voltage-gated potassium channel VGKCcomplex antibodies are defined by the radioimmunoprecipitation of Kv1 potassium channel subunits from brain tissue extracts and were initially discovered in patients with peripheral nerve hyperexcitability PNH. Over the past decade antibodies against voltage-gated potassium channels VGKCs have been reported in a number of neurologic syndromes such as neuromy-otonia limbic encephalitis and Morvans syndrome. We present a case of voltage-gated potassium channel VGKC antibody Ab syndrome which is a form of autoimmune non-paraneoplastic encephalitis that presents with acute or subacute memory loss confusion agitation and psychiatric symptoms. A radioimmunoassay RIA to detect antibodies against what was initially believed to be voltage-gated potassium channels VGKC in patients with neuromyotonia was established 20 years ago.


































Posting Komentar untuk "Voltage Gated Potassium Channel Antibody Syndrome"